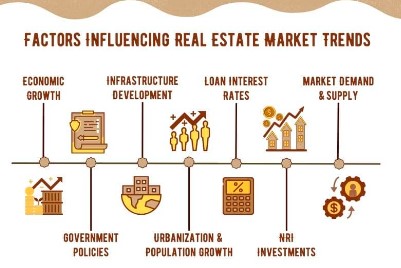
Economic shifts significantly impact real estate prices, influencing property values, rental yields, and overall market dynamics. Understanding these economic trends is crucial for investors, homeowners, and policymakers alike. This analysis explores the various economic factors affecting real estate prices, how current trends are shaping the market, and offers insights into potential future developments.
1. Interest Rates
Influence on Real Estate Prices
Interest rates are one of the most critical factors affecting real estate prices. When interest rates are low, borrowing costs decrease, making mortgages more affordable. This generally leads to increased demand for real estate, driving up property prices. Conversely, higher interest rates increase borrowing costs, reducing affordability and demand, which can lead to a decline in property prices.
Current Trends
- Global Low-Interest Environment: Over the past decade, many countries have experienced historically low interest rates due to monetary policies aimed at stimulating economic growth. This has fueled real estate booms in several markets, as cheap financing encouraged home buying and investment.
- Rising Interest Rates: As economies recover and inflation concerns rise, central banks are starting to increase interest rates. For instance, the U.S. Federal Reserve has signaled multiple rate hikes in response to inflation, impacting mortgage rates and cooling down the housing market.
2. Inflation
Influence on Real Estate Prices
Inflation affects real estate in several ways. On one hand, real estate is often seen as a hedge against inflation, as property values and rents tend to rise with inflation, preserving the purchasing power of investors\’ capital. On the other hand, high inflation can lead to higher interest rates, which can dampen real estate demand and prices.
Current Trends
- Post-Pandemic Inflation: The COVID-19 pandemic disrupted supply chains and labor markets, contributing to higher inflation rates in many countries. This has led to increased construction costs and property values.
- Central Bank Responses: To combat inflation, central banks are adjusting monetary policies, including raising interest rates, which could moderate real estate price increases by reducing borrowing capacity.
3. Economic Growth
Influence on Real Estate Prices
Economic growth generally boosts real estate markets. A growing economy increases employment, wages, and consumer confidence, leading to higher demand for residential and commercial properties. Conversely, economic downturns can lead to job losses, reduced incomes, and lower real estate demand.
Current Trends
- Recovery from COVID-19: Many economies are rebounding from the COVID-19 pandemic, leading to renewed demand for real estate. However, the pace of recovery varies across regions, affecting local real estate markets differently.
- Sector-Specific Growth: Certain sectors, like technology and healthcare, are experiencing robust growth, driving demand for specialized real estate, such as office spaces in tech hubs and medical facilities.
4. Employment Trends
Influence on Real Estate Prices
Employment trends directly impact housing demand. Higher employment rates lead to increased household formation and homebuying activity. Conversely, high unemployment can lead to foreclosures, lower home prices, and increased rental demand.
Current Trends
- Remote Work: The rise of remote work has shifted demand from urban centers to suburban and rural areas, impacting prices and demand dynamics in different regions.
- Job Market Recovery: As job markets recover from pandemic-related disruptions, demand for residential and commercial real estate is increasing, particularly in sectors less affected by remote work trends.
5. Demographic Changes
Influence on Real Estate Prices
Demographic factors, such as population growth, age distribution, and household formation rates, significantly influence real estate demand. For example, a growing population increases housing demand, while an aging population may shift demand towards specific housing types.
Current Trends
- Millennial Homebuyers: Millennials, now entering their prime homebuying years, are a significant force in the real estate market. Their preferences for urban living and sustainable homes are shaping market trends.
- Aging Population: In many developed countries, an aging population is increasing demand for senior housing and age-friendly communities, influencing development trends and property values.
6. Government Policies and Regulations
Influence on Real Estate Prices
Government policies, including tax incentives, housing subsidies, zoning laws, and rent controls, can significantly impact real estate markets. Policies aimed at boosting homeownership or affordable housing can increase demand, while restrictive zoning laws can limit supply and drive up prices.
Current Trends
- Affordable Housing Initiatives: Governments worldwide are introducing measures to increase affordable housing supply, which could moderate price growth in some markets.
- Regulatory Changes: Changes in zoning laws, environmental regulations, and property taxes are affecting real estate development and investment decisions.
7. Supply and Demand Dynamics
Influence on Real Estate Prices
Basic supply and demand principles heavily influence real estate prices. High demand and limited supply drive up prices, while oversupply and low demand lead to price decreases.
Current Trends
- Housing Shortages: Many cities face housing shortages due to population growth, limited land availability, and slow construction rates, driving up property prices.
- Construction Boom: In some regions, a construction boom is increasing housing supply, which could stabilize or reduce prices, depending on demand levels.
8. Technological Advancements
Influence on Real Estate Prices
Technology affects real estate through improved construction techniques, property management systems, and changes in demand patterns, such as the rise of smart homes and proptech.
Current Trends
- Smart Homes: Increasing demand for smart homes with advanced technologies is influencing property values, especially in urban and high-tech areas.
- Proptech: The adoption of property technology (proptech) is streamlining real estate transactions, property management, and enhancing market transparency, potentially affecting price dynamics.
9. Globalization and International Investment
Influence on Real Estate Prices
Globalization and international investment flows can significantly impact real estate markets. Foreign investment can drive up prices in popular markets, while changes in global economic conditions can influence capital flows.
Current Trends
- Foreign Investment: Despite travel restrictions, international investors continue to seek opportunities in stable and high-growth markets, influencing property prices in cities like London, New York, and Sydney.
- Geopolitical Uncertainty: Geopolitical events, such as trade wars or regional conflicts, can impact global investment patterns and real estate prices.
10. Environmental and Climate Concerns
Influence on Real Estate Prices
Environmental factors and climate change increasingly influence real estate values. Properties in areas prone to natural disasters or with poor environmental quality may see decreased demand and prices.
Current Trends
- Sustainable Development: Growing awareness of environmental issues is increasing demand for sustainable and energy-efficient properties, influencing development practices and market values.
- Climate Risks: Properties in regions vulnerable to climate change impacts, such as coastal areas, may face declining values due to increased risks and insurance costs.
Case Studies of Economic Shifts and Real Estate Prices
The Great Recession and Real Estate Crash (2007-2009)
Overview: The global financial crisis led to a dramatic decline in real estate prices, particularly in the United States, where the housing bubble burst.
Impact: The crisis caused widespread foreclosures, plummeting home values, and a credit crunch that severely limited new mortgage originations.
Recovery: Over the next decade, real estate markets slowly recovered, driven by government interventions, low interest rates, and improved economic conditions. Some markets, however, took longer to rebound than others.
COVID-19 Pandemic and Real Estate Resilience (2020-Present)
Overview: The COVID-19 pandemic caused economic disruptions, but its impact on real estate varied by market and sector.
Residential Real Estate: Low interest rates, remote work, and a desire for more space drove up home prices in suburban and rural areas, while urban markets faced price adjustments.
Commercial Real Estate: Retail and hospitality sectors struggled due to lockdowns and reduced consumer activity, while industrial and logistics properties benefited from e-commerce growth.
Long-term Effects: The pandemic accelerated trends like remote work and e-commerce, reshaping demand patterns and influencing future real estate development and investment strategies.
Future Outlook and Conclusion
As we look toward the future, several key trends are likely to shape the impact of economic shifts on real estate prices:
- Interest Rate Trajectories: Central banks\’ actions to manage inflation through interest rate adjustments will continue to influence borrowing costs and real estate affordability. Investors should monitor interest rate policies closely.
- Sustainable and Resilient Development: Growing emphasis on sustainability and resilience in real estate development will drive demand for energy-efficient properties and influence long-term value appreciation.
- Technological Integration: The integration of technology in real estate, from smart homes to proptech solutions, will continue to transform market dynamics, improving efficiency and transparency.
- Urbanization and Demographic Shifts: Urbanization trends and demographic changes, such as aging populations and millennial homebuying, will shape housing demand and development priorities.
- Global Economic Integration: Globalization and international investment flows will remain significant, with geopolitical events and economic policies influencing capital movements and real estate markets.
- Climate Adaptation: Real estate markets will increasingly factor in climate risks, with properties in vulnerable areas facing greater scrutiny and potentially lower values.
Conclusion
The interplay between economic shifts and real estate prices is complex and multifaceted. Factors such as interest rates, inflation, economic growth, employment trends, demographic changes, government policies, supply and demand dynamics, technological advancements, globalization, and environmental concerns all play crucial roles in shaping real estate markets.
Understanding these influences is essential for investors, homeowners, and policymakers to navigate the real estate landscape effectively. By staying informed about current trends and anticipating future developments, stakeholders can make strategic decisions that align with their goals and mitigate risks.
As the global economy continues to evolve, the real estate market will undoubtedly face new challenges and opportunities. Adapting to these changes and leveraging insights from past trends will be key to thriving in this dynamic environment. Whether it\’s through careful analysis of economic indicators, embracing technological advancements, or prioritizing sustainable development, the ability to respond to economic shifts will determine success in the ever-changing world of real estate.
For more on the Impact of Economic Shifts on Real Estate Prices check out this detailed article on the factors affecting real estate markets. Also see our blog section to get access to other resources